Table of Contents
In Egyptian mythology, the goddess Isis was a significant deity, known for her role in the royal affairs of the gods. She was one of the most famous figures in Egyptian mythology and was part of the Ennead and the cult of Heliopolis.
Let’s take a closer look at her myth.
Who Was Isis?
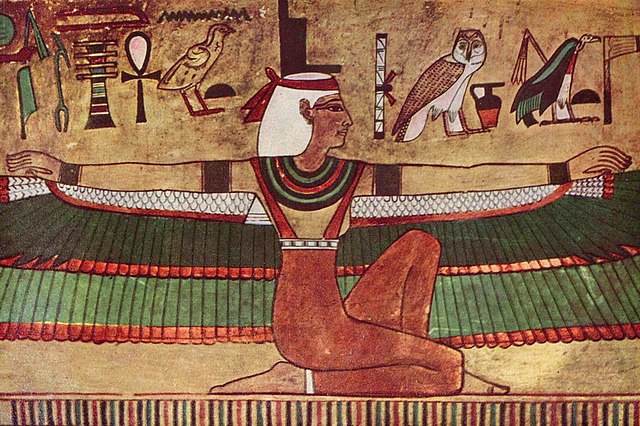

Isis was the daughter of Nut, the goddess of the sky, and Geb, the god of the earth. Isis was the protectress of women and children and a mighty queen during the reign of Osiris, her husband, and her brother. Additionally, she was the goddess of the moon, life, and magic, and also presided over marriage, motherhood, spells, and healing. Her name stands for ‘throne‘ in ancient Egyptian language.
Isis represented almost every other goddess of the Egyptian Pantheon, for she was the most important female deity of the culture. The other deities appeared in many cases as mere aspects of Isis. Isis was the ultimate mother goddess, known for her close ties to her son and the troubles she went through to conceive, deliver and protect him.
Below is a list of the editor’s top picks featuring the statue of Isis goddess.
Depictions and Symbols of Isis

Isis’ depictions showed her as a youthful woman wearing a sheath dress and holding an ankh in one hand and a staff in the other. She was also often depicted with large wings, perhaps as an association with kites, birds known for their wailing cries. Some other depictions show Isis as a cow (signifying her maternal and nourishing status), a sow, a scorpion and sometimes a tree.
From the time of the New Kingdom, Isis was often depicted with attributes characteristic of Hathor. These included portrayals with cow horns on her head, with a sun disk at the center, and carrying a sistrum rattle.
A symbol closely associated with Isis is the Tyet, also known as the Knot of Isis, which resembles the ankh symbol and represents welfare and life. More obscure are its associations with the blood of Isis, and while it is unclear, it may be linked to the magical properties Isis’ menstrual blood was thought to have.
Family of Isis
As the daughter of Nut and Geb, Isis was a descendant of Shu, Tefnut, and Ra, the primordial deities of ancient Egypt, according to the Heliopolis cosmogony. She had four siblings: Osiris, Set, Horus the Elder, and Nephthys. Isis and her siblings became the principal gods of human affairs since they reigned on earth. Isis and Osiris would marry and become the rulers of Egypt in a mythical time. Together, they birthed Horus, who would later succeed his father to the throne by defeating his uncle, Set.
The Role of Isis in Ancient Egypt

Isis was a secondary character in the early myths, but over time, she grew in status and importance. Her cult even transcended Egyptian culture and went on to influence Roman tradition, from where it spread across the world. Her powers went beyond those of Osiris and Ra, making her perhaps the mightiest deity of the Egyptians.
Isis’ roles included:
- Mother – She was the protectress and the main help of her son Horus after Set tried to take the throne from Osiris. Her devotion and loyalty to her son made her a role model for mothers everywhere.
- Magical healer – Isis was the greatest healer in the world, for she had learned the secret name of Ra, and that had given her special powers. As the goddess of magic, Isis played a central role in the mystical affairs of Ancient Egypt.
- Mourner – Egyptians employed mourners to attend funerary ceremonies, and Isis was considered the patron of mourners due to being the widow of Osiris. This fact made her a major deity in connection with the rites of the dead.
- Queen – Isis was the queen of the universe during the reign of Osiris, and after his demise, she never stopped looking for him. She was devoted to her husband to the point where she briefly brought him back from the dead with her magic.
- Protectress – She was the protectress of women, children, and marriage. In this sense, she taught women throughout all Egypt how to weave, cook, and make beer. People invoked her and asked for her favor to help the sick. In later times, she became a deity of the sea and the protectress of the sailors.
- Pharaoh’s Mother/Queen – Because rulers were associated with Horus during life and with Osiris after death, that made Isis the mother and queen of the rulers of Egypt. This gave her great importance as the nourisher, protector and later, as the companion of the pharaohs.
The Myth of Isis
Isis is a central figure in the myth of Osiris, one of the most famous stories of Egyptian mythology. It’s Isis who brings her husband back to life using her magic, and later bears the son who goes on to avenge his father and take back his throne.
Isis and Osiris
As the queen and wife, Isis was involved with the prosperous era of the reign of Osiris. However, this would come to its end when Set, the jealous brother of Osiris, plotted against him. Set had a customized chest made so that Osiris could fit within it perfectly. He organized a contest and said that anybody who would fit inside the beautiful wooden box could have it as a prize. As soon as Osiris entered it, Set closed the lid and threw the coffin into the Nile.
When Isis discovered what had happened, she wandered the land looking for her husband. The other deities took pity on her and helped her find him. In the end, Isis found the body of Osiris in Byblos, in the coast of Phoenicia.
Some stories say that when Set found out about this, he dismembered Osiris and scattered his body throughout the land. However, Isis was able to gather these parts, resurrect her loved one and even conceive her son Horus. Osiris, never completely alive, had to go to the Underworld, where he became the god of death.
Isis and Horus

Isis would protect and hide Horus from Set during his childhood. They stayed in the marshes, somewhere in the Nile delta, and there, Isis protected her son from all the dangers around. When Horus finally came of age, he defied Set to take his place as the rightful king of Egypt.
Although Isis was always on Horus’s side, in some later accounts of the myth, she took pity on Set, for which Horus beheaded her. However, she would not remain dead. She came back to life through magic and reconciled with her son.
The Intervention of Isis
After many years of conflict between Horus and Set over the throne of Egypt, Isis decided to take action. She disguised herself as a widow and sat outside the place where Set was staying. As soon as Set passed by her, she started crying helplessly.
When Set saw her, he asked what was wrong. She told him the story of how a stranger had usurped her late husband’s lands and left her and her son destitute. Set, not recognizing her or the story as his own, vowed that as the king, he would make the man pay for his actions.
Isis then revealed herself and used Set’s words against. Him. She told the other gods what Set had done and what he had pledged to do. After that, a council of gods decided to give the throne to the rightful heir Horus, and Set was exiled to the deserts, where he became the god of chaos.
Worship of Isis
The cult of Isis began much later than that of most other deities of Ancient Egypt. She did not have temples dedicated to her until the Late Period when King Nectanebo II built one in the central Nile delta.
Isis’ worship went beyond Pharaonic Egypt, and she became a highly revered goddess during the Greek rule in Alexandria, where she had several temples and cults. She was associated with the goddess Demeter, and she remained a central figure in the Greco-Roman era.
Isis had cults in Iraq, Greece, Rome, and even England. Later, Isis became a main deity of paganism because of her associations with magic and resurrecting the dead. She continues to be a notable figure in Neo-Paganism.
The Roman emperors started closing all pagan temples that worshipped deities other than those of Christianity. The temples of Isis were among the last to shut down in the mid-6th century, after 2000 years of worship.
Isis and Christianity
Parallels have been drawn between Isis, Osiris and Horus (known as the Abydos Triad) with Christianity. Isis had associations with the Virgin Mary. They were both known as the mother of god and the queen of heaven. Some authors believe that the early depictions of Isis feeding the baby Horus might have influenced the portrayals of Jesus and the Virgin Mary.
Facts About Isis

Isis is the goddess of magic, fertility, motherhood, the afterlife and healing.
Isis meant throne in the ancient Egyptian language.
The wings of Isis may represent those of kites, birds who cry out like wailing women. This could be because of Isis’ cries during the time she looked for her husband.
Isis became a prominent figure in Egyptian mythology and her worship spread to other cultures. She was associated with Demeter (Greek), Astarte (Middle East) and Fortuna and Venus (Roman).
These are two distinct goddesses but had been associated and even conflated in later myths.
Isis was able to magically heal people magically, and had the power of protection.
Isis was the most popular and powerful female goddess of ancient Egypt as she was associated with most aspects of daily life.
Isis’ husband is Osiris.
Isis is the child of Nut and Geb.
Isis is the mother of Horus, whom she conceived under miraculous circumstances.
Wrapping Up
Isis’ cult spread beyond the frontiers of ancient Egypt, and her role in the affairs of mortals and gods gained significant influence. She was the foremost female figure of Egyptian mythology, seen as the mother to the rulers of Egypt.