With so many people in the world, it’s only natural for us to divide into different groups, with each group based on different religious beliefs and desires. As a result, no matter where you go, every country in this world will always have large groups of people that follow different organized religions.
Since China’s the most populated country in the world, the Chinese have various religions which people follow. In China, there are three principal philosophies or religions: Taoism, Buddhism, and Confucianism.
Taoism and Confucianism originated in China. Their founders are Chinese philosophers that believed in the harmony between humans and nature instead of considering humans as superior beings. Buddhism, on the other hand, originated in India, but was adopted by China and gained a steady following.
Despite their differences and continual clashes, all of these religions had an impact on Chinese culture, education, and society. With time, these religions overlapped, creating a new culture and belief system which the Chinese called “San Jiao.”
Apart from these three primary philosophies, there have been other religions that were introduced to China. These also influenced Chinese society and further added to its diversity.
So, are you excited to learn what they are?
The Three Pillars of Chinese Religious Culture
The three main philosophies in China were extremely important to their ancient era. As a result, the Chinese integrated Confucianist, Buddhist, and Taoist practices into most aspects of their society and culture.
1. Confucianism
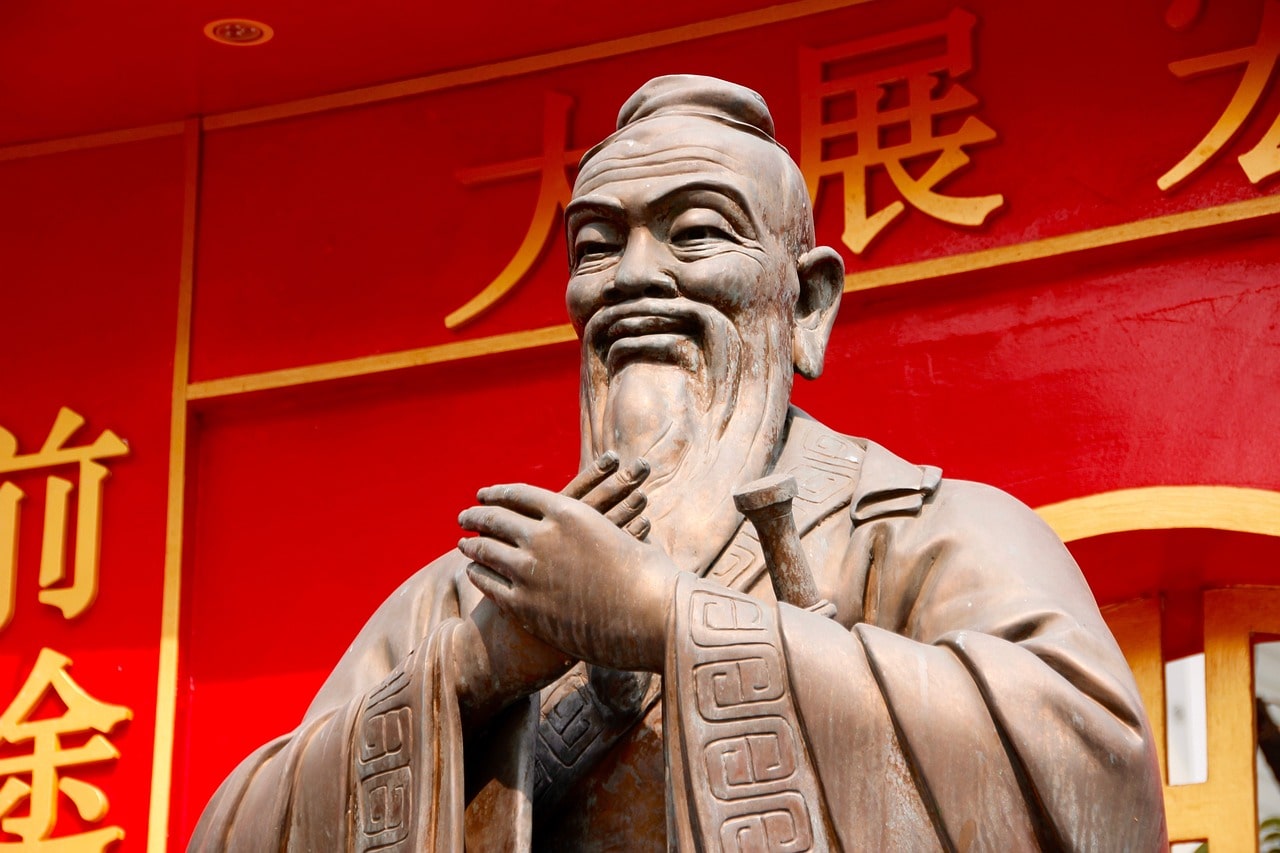

Confucianism is more of a philosophy than a religion. It’s a way of life that was adopted by the people from ancient China and its practices are still followed, to this day. This belief system was introduced by Confucius, a Chinese philosopher, and politician who lived during 551-479 BCE.
During his time, he witnessed the decline of many Chinese principles because of the lack of accountability and morality among his people. As a result, he developed a moral and social code that he considered could help society achieve a harmonic balance. His philosophy presented people as beings with inherent obligations and mutual dependency.
Some of his teachings encouraged people to treat others how they want to be treated, i.e., to be kind, and to be diligent in their duties so society could flourish and become more efficient.
Unlike many philosophies, Confucianism doesn’t focus on the spiritual plane, nor god or deities. Instead, Confucius directed this philosophy solely to human behavior, encouraging self-ownership and making people responsible for their actions and everything that happens to them.
Nowadays, Chinese people still maintain his teachings and allow the overall principles of his philosophy to be present in their lives. They apply the concepts of Confucianism to aspects such as discipline, respect, duties, worship of ancestors, and social hierarchy.
2. Buddhism
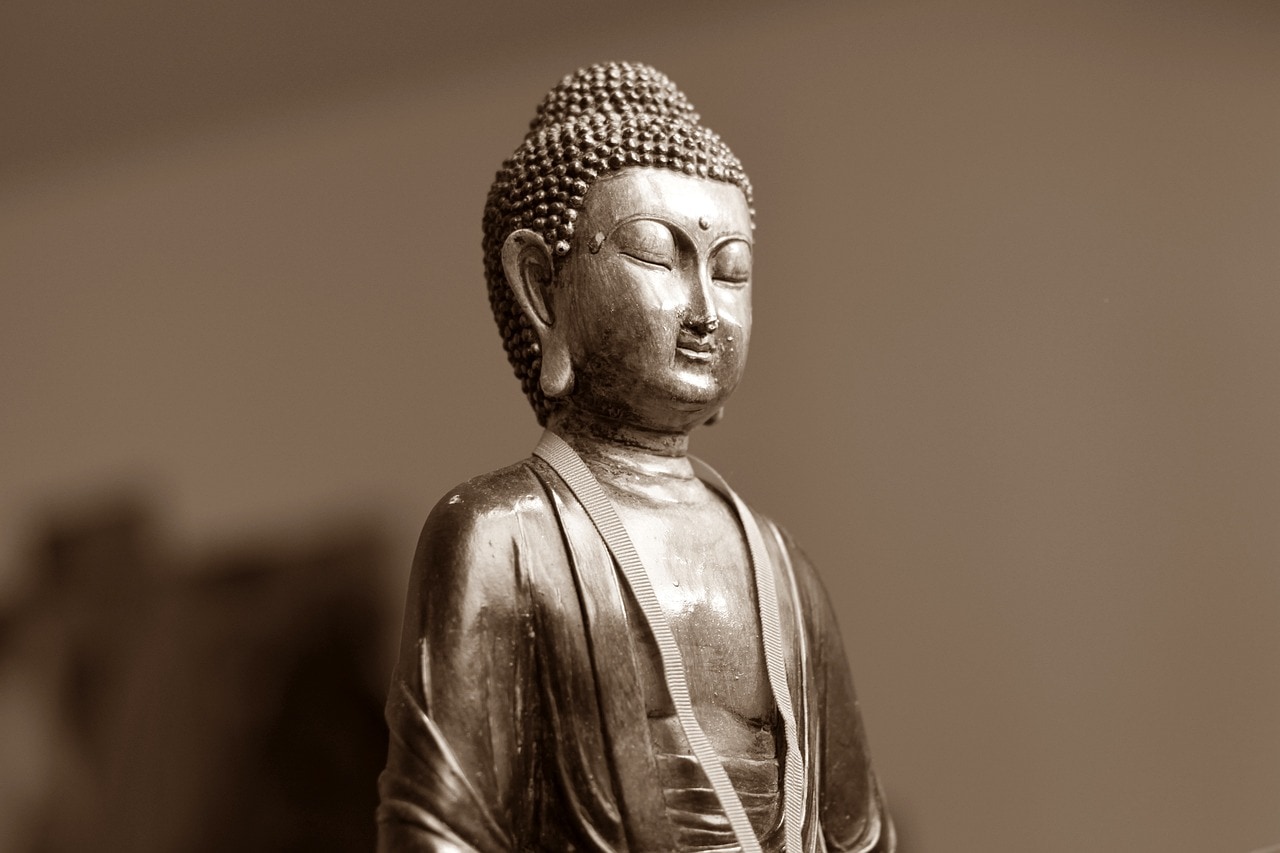

Buddhism is an Indian philosophy that was introduced by Siddhartha Gautama, who the Buddhists consider to be the Buddha (The Enlightened one), during the 6th century BCE. Buddhism centers itself around self-development through meditation and spiritual labor to reach enlightenment.
The Buddhist beliefs include reincarnation, spiritual immortality, and the fact that human life is full of uncertainty and suffering. For this reason, Buddhism encourages its followers to attain nirvana, which is a state full of joy and tranquility.
Like many other philosophies and religions, Buddhism divides itself into branches or sects. Two of the most established are Mahayana Buddhism, which is the most popular in China, along with Theravada Buddhism.
Buddhism spread to China during the 1st century AD and became more prevalent thanks to Taoism, mostly because Buddhism and Taoism have very similar religious practices.
Although followers of Buddhism and Taoism had their fair share of conflicts during one point in history, the competition only made both of them more prominent. Eventually, Taoism and Buddhism, together with Confucianism, unified to make what we know today as “San Jiao”.
3. Taoism

Taoism, or Daoism, is a Chinese religion that started shortly after Confucianism. This religion centers more around the spiritual aspects of life such as the universe and nature, with its primary tenets encouraging followers to attain harmony with the natural order of life.
Taoism encourages its followers to relinquish their desire for control and accept everything that life brings their way, such that its followers can reach the extremely desired harmony: a state of mind referred to as “non-action.”
This is why people often believe that Taoism is the opposite of Confucianism. While Taoism preaches “going with the flow,” Confucianism calls its people to action if they are to manifest the changes they want to see in their lives
Another interesting objective of Taoism is to reach physical longevity and spiritual immortality. The way to do that is to become one with nature and reach enlightenment. Taoists hold this as something of utmost importance.
Since Taoism focuses on nature and natural elements, it has contributed a great deal to the development of Chinese medicine and science throughout history, all thanks to Taoists that followed its teachings for developing a way to extend the longevity of human life.
The Lesser-Known Religions of China
Although the above three religions are the most prominent across China, several other smaller communities also came into existence. These belief systems were mostly introduced by traditional western missionaries.
1. Christianity
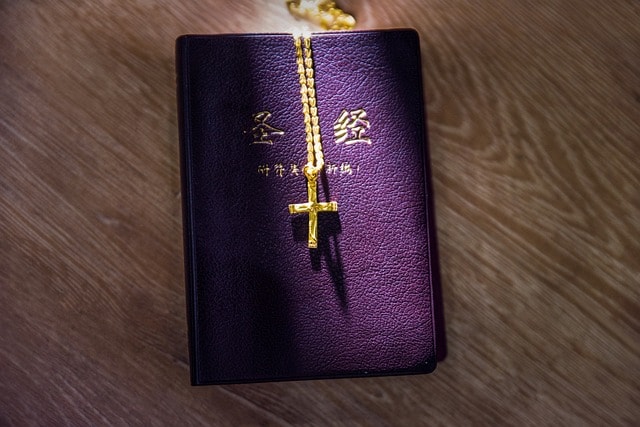

Christianity and all of its forms are focused on worshiping Christ and following their holy written code, which is the Bible. Christianity was introduced in China during the 7th century by a missionary who journeyed from Persia.
Nowadays, several catholic Churches are well-known religious landmarks. Considering the Christian population in China, it is estimated that there are around four million Catholics and more than five million protestants.
2. Islam

Islam is a religion that focuses on following Allah’s instructions, from their holy book: the Quran. Islam spread to China, from the Middle East, during the 8th century.
Nowadays, you can find Chinese Muslims in northwest China. They are in the Ganxu, Xinjiang, and Qinghai provinces, along with small Islamic communities in the big cities. Even today, Chinese Muslims adhere to the teachings of Islam, religiously. You can find several iconic “Chinese mosques” that are perfectly preserved.
Wrapping Up
As you can see, the majority of the Chinese people don’t follow Western religions since they have developed their own philosophies and belief systems. Nonetheless, the teachings and practices of all these religions, big or small, have combined and permeated into Chinese society.
Hopefully, after reading this article, you will have a greater understanding of Chinese culture. So, if you ever decide to visit China, you will be better equipped to navigate its rules and society.