The sun played a central role in Egyptian mythology since its beginning, with several important symbols associated with it. One such symbol was the Winged Sun, a powerful symbol of royalty, power, divinity and the triumph of order over chaos, associated with several deities of ancient Egypt. Its connections with power and royalty gave it unparalleled significance.
What Was the Winged Sun?

The Winged Sun is a symbol that likely existed even before the Egyptian civilization. In Egyptian art, the Winged Sun is attested to since the Old Kingdom, where its first appearances decorated the coffins of kings and queens, and it remained relevant throughout the history of this culture.
The representations of this symbol show it as its name indicates – a sun or solar disk in the center with spread wings on either side. In many cases, the Winged Sun also had Egyptian cobras flanking it. This symbol represented royalty, power, and divinity in Ancient Egypt, but it also held significance in other Ancient Near Eastern regions like Anatolia, Mesopotamia, and Persia.
The Winged Sun in Ancient Egypt
Due to its associations with the sun, the Winged Sun was linked to the sun god Ra. However, its most common associations were with Horus, the falcon god.
Originally, the Winged Sun was the symbol of Behdety, the god of the midday sun worshipped in Lower Egypt. Only later, this god became an aspect of Horus, so the Winged Sun became associated with him. When combined with Behdety, he became known as Horus of Behdet or Horus of Edfu. Since Horus was the protector of the kingship and a divine ruler, the Winged Sun had associations with these traits too.
In the terrible fight between Horus and Seth for the rule of Egypt, Horus flew to battle and opposed Seth in the form of the Winged Sun. The most famous representation of the Winged Sun is still present in the lintel of the main entrance to the Temple of Edfu, in Upper Egypt. In its female form, the Winged Sun could represent the goddess Hathor.
The Symbolism of the Winged Sun
Apart from the symbolism given by its connection with Horus and the sun, the Winged Sun represented other important concepts for the Egyptians.
The symbol became an amulet of protection over time. Since Horus had defeated the mighty antagonist Seth in the form of the Winged Sun, this symbol became associated with protection against the forces of chaos. From the Middle Kingdom onwards, the Egyptians used the Winged Sun as an amulet in tombs and in the sarcophagi of the pharaohs for protection.
In Ancient Egypt, the Winged Sun was a symbol of the power of the sun, royalty, the soul, and eternity. In this sense, the Winged Sun became an attribute of different deities in the myths. Its veneration in Ancient Egypt grew more important over the millennia.
This symbol was deemed as holding many powers and was related to the eternal fight between order and chaos, light, and darkness. The Winged Sun shed light over the world and protected the skies and the universe against those who wanted to cause pain and suffering.
The sun itself was a symbol of nourishment, power, and life. Without the sun, life could not exist the way it does, and the world would be immersed in eternal darkness. This idea strengthens the symbolism of the Winged Sun as a powerful apotropaic amulet.
The Winged Sun Outside Ancient Egypt
The Winged Sun was a significant aspect of different cultures outside Ancient Egypt. With the myth of Horus and Seth as inspiration, the Winged Sun represented the good fighting against the bad.
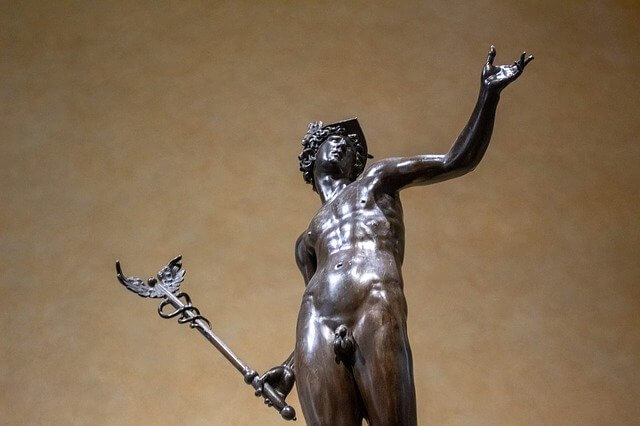

This was the case in Greek mythology with the Olympians fighting Typhon, a god Plutarch associated with the Egyptian Seth, and in Christianism with God fighting Satan. The Winged Sun always stood on the side of the good and the light. The symbol of the Winged Sun also appears in Greek mythology as part of the staff of Hermes.
In Mesopotamia, this symbol was linked to majesty and royalty, and in Hebrew culture, with righteousness. Other cultures and groups, such as the freemasons, used this symbol too. There are references to the Winged Sun in the Christian Bible, referring to the rise of good powers and protection under its wings. The Roman empire also adopted the Winged Sun, as the cult of Sol Invictus came to popularity in the times of Aurelian (ca. 274 AD).
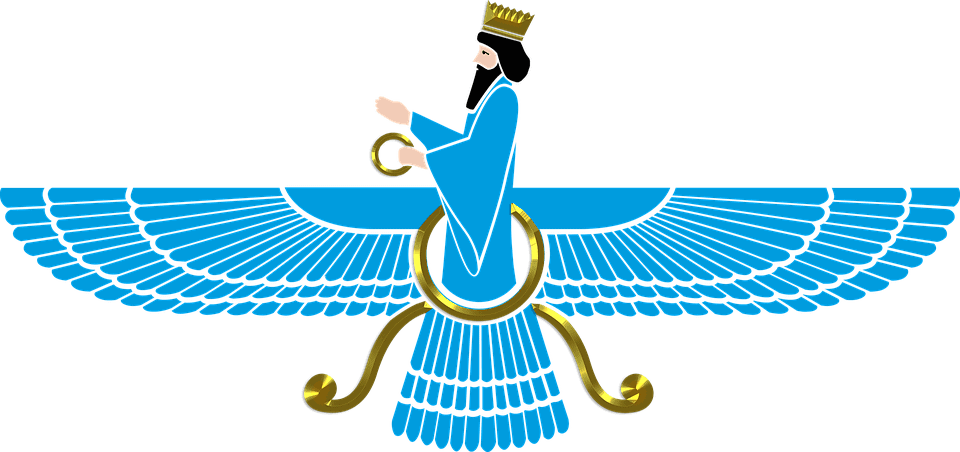
The Winged Sun evolved into the Faravahar, a symbol of the Persian religion Zoroastrianism. This symbol represented the principle tenets of their religion and was a symbol of divine rule and power.
In Brief
The Winged Sun was an ancient symbol that represented divinity, royalty, power and the light and goodness of the world. This symbol was significant inside and outside the frontiers of Ancient Egypt. The Egyptians worshipped it to receive its protection. Present from very early in their history, the Winged Sun remained a central part of Egyptian culture for millennia.