Table of Contents
Apples have played a significant and often symbolic role in many ancient myths, fairytales and stories. There’s something about this fruit that sets it apart from others, making it a prominent motif and a meaningful product of the natural world.
With that said, let’s take a closer look at the symbolic meaning of apples and the role it’s played in global culture over the years.
Symbolic Significance of Apples

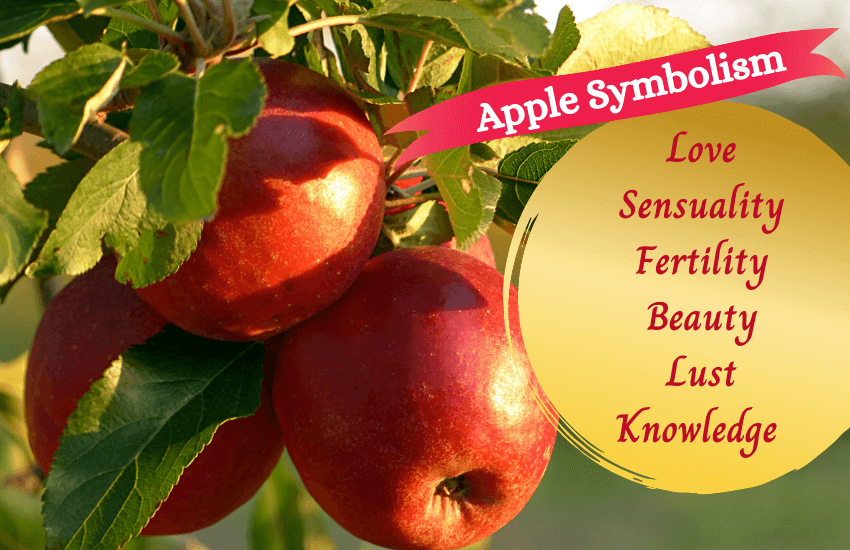
The apple’s symbolism dates back to ancient Greek times and is typically connected to emotions of the heart. These include love, lust, sensuality and affection.
- Symbol of love: The apple is known as the fruit of love and has been used since time immemorial to express affection and passion. In Greek mythology, Dionysus offers apples to Aphrodite, in order to win her heart and love.
- Symbol of sensuality: Apples are often used in paintings and artworks as a symbol of desire and sensuality. The Roman Goddess Venus is often depicted with an apple to express love, beauty, and desire.
- Symbol of a positivity: The apple is a symbol of goodness and positivity for in Jewish culture. During the Rosh Hashanah, or the Jewish New Year, it is custom for Jewish people to eat apples immersed in honey.
- Symbol of feminine beauty: The apple is a symbol of feminine beauty and youth in China. In China, apple blossoms represent feminine beauty. In northern China, the apple is a symbol of Spring.
- Symbol of fertility: The apple has been used as a symbol of fertility across many cultures and traditions. In Greek mythology, Hera received an apple during her engagement to Zeus, as an emblem of fertility.
- Symbol of knowledge: The apple is a symbol of knowledge, wisdom, and education. In the 1700’s, apples were gifted to teachers in Denmark and Sweden, as a mark of their knowledge and intellect. This tradition began to be followed in the United States from the 19th century onwards.
Cultural Significance of Apples
Apples are a part of several cultural and spiritual beliefs and have both positive and negative meanings. Some of the cultural significations of apples are as follows:
- Christianity
According to the old testament, the apple symbolized temptation, sin, and the fall of mankind. The forbidden fruit consumed by Adam and Eve was believed to be an apple. In the biblical Songs of Solomon, the apple is used as a symbol of sensuality. In the New Testament, however, the apple is used in a positive sense. Jesus Christ is sometimes portrayed with an apple in his hand, as a symbol of revival and redemption. The New Testament also uses the phrase “apple of my eye” to denote strong love.
- Cornish Beliefs
The Cornish people have a festival of apples, with several games and customs related to the fruit. During the festival, large polished apples, are gifted to friends and family, as a symbol of good luck. There is also a popular game where the participant has to catch apples with their mouths. Cornish men and women take back the festive apples and keep it under their pillows as it’s believed to attract a suitable husband/wife.
- Norse Mythology
In Norse mythology, Iðunn, the goddess of eternal youth, is associated with apples. Iðunn keeps the golden apples to bestow gods with immortality.
- Greek mythology
The motif of the apple recurs throughout Greek mythology. The golden apples in Greek tales come from the grove of goddess Hera. One of these golden apples, also known as the apple of discord, lead to the Trojan war, when Paris of Troy gifted the apple to Aphrodite and kidnapped Helen of Sparta.
The golden apple is also depicted in the myth of Atlanta. Atlanta is a quick footed huntress who proposed to marry one who could run faster than her. Hippomenes had three golden apples from the garden of Hesperides. As Atlanta ran, he dropped the apples, which distracted Atlanta, causing her to lose the race. Hippomenes then won her hand in marriage.
History of The Apple
The ancestor of the domesticated apple is the Malus Sieversii, a wild apple tree found in the Tian Shan mountains, Central Asia. Apples from the Malus Sieversii tree were plucked and taken onto the Silk Road. During the long journey, several varieties of apples fused, evolved, and hybridized. These newer forms of apples were then taken via the Silk Road to different parts of the world, and they gradually became a common fruit in local markets.
Apples reached different regions at different times of history. In China, apples were consumed about 2000 years ago, and were predominantly used in desserts. These apples were much softer, being the hybrids of the M. baccata and M. sieversii varieties. In Italy, archaeologists have discovered ruins which suggest the consumption of apples from 4000 BCE. In the Middle East, there is evidence to say that apples were cultivated and eaten from the third millennium BCE. Apples were brought into North America in the 17th century, by European colonialists. In America and the rest of the world, apples were largely stored in attics or cellars.
Interesting Facts About Apples
- Apple Day is a festival held on October 21, which supports local culture and diversity.
- Apple trees live for about 100 years.
- Apples are made of 25% air and can float easily in water.
- Native Americans who think and act like white people are called apple Indians, symbolizing that they’ve forgotten their cultural roots.
- Apple bobbing is one of the most famous games of Halloween.
- Malusdomesticaphobia is the fear of eating apples.
- Isaac Newton discovered the law of gravity after an apple fell on his head.
- There are about 8,000 varieties of apples worldwide.
- The bible does not state that the apple is the forbidden fruit, but believers have formed such an interpretation.
- Apples induce mental alertness and sharpness.
- According to current records, China is the largest producer of apples in the world.
In Brief
The apple is a versatile and complex fruit with several symbolic meanings. It can mean love, sin, knowledge, or sensuality. It remains one of the most symbolic of all fruits, with a prominent role in several belief systems and cultures.