Table of Contents
Like most countries, a lot of thought and effort went into choosing a final design for Australia’s flag. Inaugurated in 1901, the Australian flag became among the country’s most important national symbols. It continues to be a strong expression of Australian pride and identity as it is displayed in schools, government buildings, sporting events, and more. Ever wondered what the elements in Australia’s flag symbolize? Read on to learn about the story behind its distinct design.
The History of Australia’s Flag
Colonized in 1788 by Britain, Australia consisted of 6 different colonies, which eventually united and became an independent nation in 1901. While the circumstances of Australia’s colonization were pretty similar to that of the US, one main difference was that Australia remained a member of the British Commonwealth after it was federated, and the Queen of England continued to have power over Australia’s affairs.
The influence of the Queen of England on Australia can be seen in the history of Australia’s flag as well. Since it remained a part of the British Commonwealth, the country needed approval for the final design of its flag before they could officially adopt it.
Australia’s flag was introduced to the world on January 1, 1901, the day when its colonies were federated to form an independent nation. Rt. Hon. Sir Edmund Barton, the country’s first Prime minister, announced a flag-making competition and urged citizens to submit their proposed designs.
Red or Blue Ensign?
A committee went through around 30,000 design submissions. Interestingly, 5 of the designs looked extremely similar to each other. They all won first place and their makers shared the prize money of 200 pounds. Dubbed the Commonwealth Blue Ensign, the flag was flown at the Exhibition building in Melbourne for the first time on September 3, 1901.
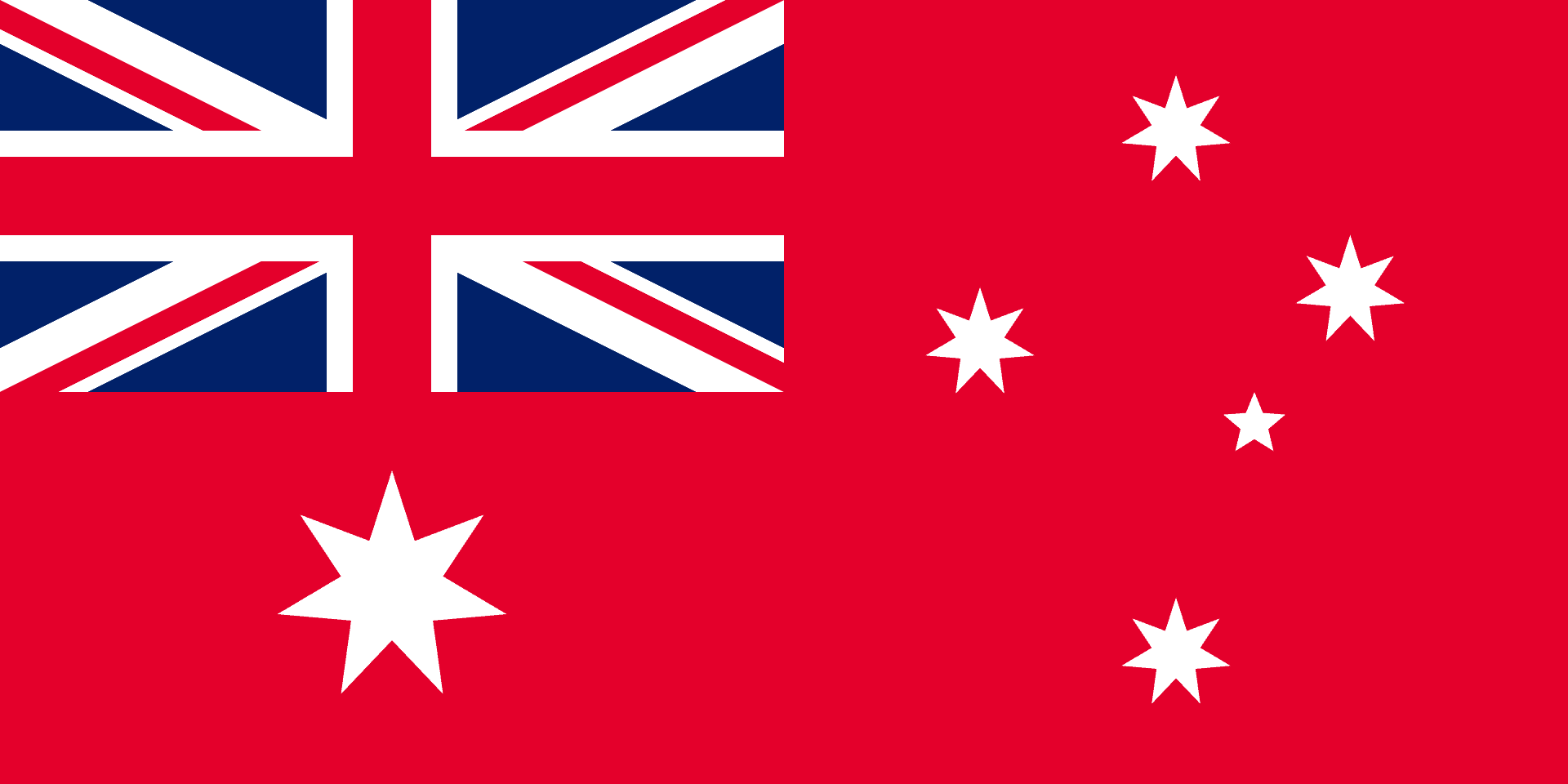
The Commonwealth Blue Ensign had two versions. The first one had the blue ensign against a blue background, while the second had the red ensign against a red background. British custom dictated that private citizens cannot fly the Blue Ensign and that its use should be reserved for forts, naval vessels, and government buildings.
This prompted Australian citizens to fly the second version of the flag, the one with the red ensign, in their homes. This eventually led to confusion on what Australia’s official flag was. The Flag Act of 1953 affirmed that Australia’s official flag was the Blue Ensign and finally allowed private citizens to display it in their homes. This took its red version out of the picture.
The Meaning of Australia’s Flag
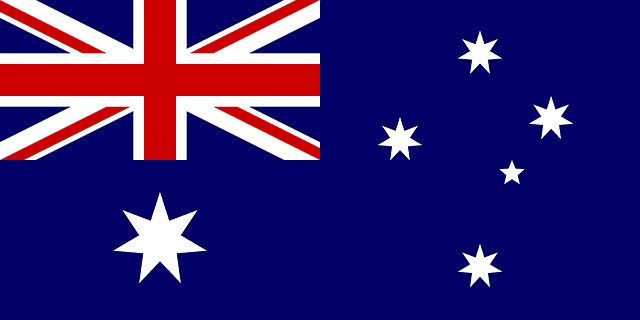
Australia’s flag has a distinct design that consists of crosses and stars. As the country’s most important national symbol, it was thought to represent Australian citizens regardless of their race, background, or religion. It continues to serve as a reminder of the nation’s heritage and the contribution of the past and present generations to nation-building. Each symbol in Australia’s flag means something. Here’s a list of what each symbol represents.
The Constellation of Stars
The flag of Australia has 6 distinct stars, with each one representing the territories that make up the nation. The biggest star is referred to as the Commonwealth Star and became the Australian Federation’s emblem. While its 6 points represent the 6 different states of Australia, the 7th one represents all other remaining Australian territories.
The smaller stars on the right side of the flag features the Southern Cross. This constellation symbolizes Australia’s geographical location. It also relates to various indigenous legends and reminds the Australian people of their rich Torres Strait and Aboriginal heritage.
The White and Red Crosses
The Union Jack (a.k.a. the British flag) occupies a prominent position on the upper left corner of the Australian flag. It consists of three different crosses – those of St. George, St. Patrick, and St. Andrew. These represent the various ideals and principles on which the Australian nation was founded and built upon, including the rule of law, parliamentary democracy, and freedom of speech.
The red cross of St. George in the middle of the flag represents the flag of England, while the cross of St. Andrew represents the flag of Scotland. The red cross of St. Patrick that intersects the crosses of St. Andrew and St. George represents the flag of Ireland. Together, these three crosses of the Union Jack represent the long and rich history of the British settlement.
In 1998, an amendment was added to the Flags Act of 1953 to make sure that the country’s national flag could only be changed with agreement of its citizens. While the debate on whether Australia needs a new flag that does not have the Union Jack persists, the current Australian flag continues to represent the rich history and culture of Australia.
Other Flags of Australia
While Australia has long settled on an official flag design, it would be interesting to note that the country also used a number of other flags. Here is a list of those flags.
The Queen’s Personal Flag
The personal Australian flag of the Queen of England is reserved for her use when she is in Australia. Approved in 1962, the flag is based on the coat of arms of Australia. It features a rectangular shape with an ermine border, Australia’s coat of arms, and a huge 7-pointed gold star at its center. While the golden star represents the Commonwealth, the ermine border around the badges represents the federation of each state.
The Governor-General’s Flag
The flag of the Governor-General of Australia is an official flag of Australia. It has a royal blue color and bears a golden Royal Crest. The words Commonwealth of Australia are written in bold letters on a golden scroll position below the crest. This flag is flown every time the Governor-General is in residence.
The “Eureka” Flag
The Eureka flag is one of Australia’s unofficial flags. It sports a white cross against a blue background with five white, 8-pointed stars – one in the center and one at the end of each arm of the cross. A group of rebels who were protesting the cost of licenses at the Eureka Stockade first used this flag in 1854 in Victoria, Australia. Many trade unions and militant groups have adopted this flag as a symbol of their eagerness to defend their rights.
The Flag of Aboriginal Australia
The Flag of Aboriginal Australia was first flown in 1971 to represent the Aboriginal Torres Strait Islanders of the country. It has three prominent colors – a red lower half and a black upper half as its background, and a large yellow circle in the center. While the black half represents Australia’s Aboriginal people, the red half symbolizes their blood. The yellow circle depicts the power of the sun.
The Flag of the Republican Movement
Over the years, Australia has launched several campaigns to come up with a new flag design, one that would truly represent the Australian identity. Some suggest that the Eureka flag be used, while others propose a blue flag with an enlarged Southern Cross.
Wrapping Up
Australia’s flag demonstrates its close ties with the former British empire and celebrates its history. There continues to be some controversy about maintaining the current flag with its emphasis on Australia’s connection with the British, but for now, it remains one of the most important national symbols of Australia.