Table of Contents
Blue: a rare color in nature and the favorite of many people around the world. It’s one of the three primary colors, used for many purposes including textiles, jewelry, art and decoration. But interestingly, for much of recorded history, blue remained an unimportant color, difficult to obtain and rarely used. Today, it’s one of the most popular colors in the world.
Here’s a quick peek at the history of the color blue, what it signifies, and how it’s used today.
The History of the Color Blue

If you ask someone what their favorite color is, chances are they’ll say blue. While we do have large expanses of blue in the sky and the seas, blue objects in nature are quite rare. As a result, blue pigments were rare and made blue a difficult color to obtain for early people.
- Blue in the Ancient World
The color blue has been of great importance in art and decoration since the ancient times, but it actually came into use much later than the other primary colors. There are many cave paintings dating from the Paleolithic period, created using colors such as blacks, reds, ochres and browns but blue is nowhere to be seen.
Although the other colors including purple and pink were used for dyeing fabric in the ancient items, blue was not used. It’s likely that the color wasn’t in use because of how difficult it was to create good quality pigments and dyes. The earliest blue dyes (around 6000 years ago) were made using plants. Some pigments were made from certain minerals like lapis lazui or azurite.
In Afghanistan, the semi-precious stone Lapis Lazuli had been extensively mined for over 3000 years and exported to many countries around the globe. The Iranians and Mesopotamians put this stone to good use by making vessels and jewelry from it. In Greece, the color was so unimportant that there wasn’t even a name for it.
- Blue in Egypt
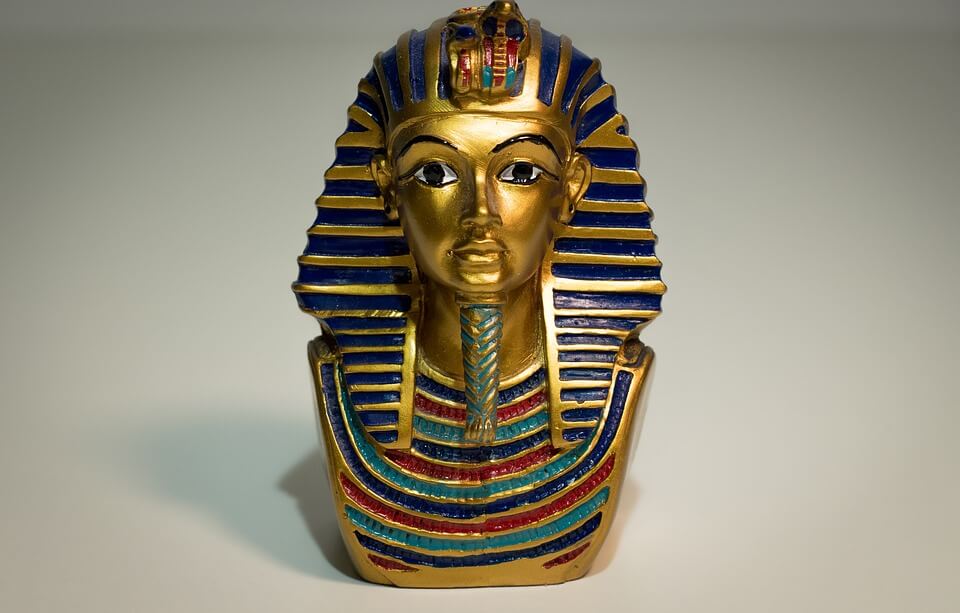

The Egyptians used lapis lazuli on the funeral mask of the Pharaoh Tutankhamun. Later on, they began to produce their own blue pigment by grinding together silica, lime, alkalai and copper and heating it up to about 900oC.
The pigment was known as Egyptian blue and is considered the first synthetic pigment. It was then that the Egyptian word for ‘blue’ first emerged. Egyptian blue was used widely for various purposes including painting wood, canvas and papyrus and later on in pottery and the making of figurines.
Gradually, Egyptian blue dyes began to spread throughout the world to Rome, Mesoamerica and Persia. These dyes were so expensive that only royalty were able to afford them and blue remained a rare color for many centuries.
- Blue in Ancient Rome
In Rome blue was the color of the garments worn by the working class whereas the nobility wore white, red, black or violet. However, they used blue extensively for decorating and made the dye from indigo mixed with the imported Egyptian blue pigment.
In Pompeii, the walls of Roman villas had beautiful blue skies painted on them and the pigments were available in the shops of merchants who sold colors.
- Blue in the Middle Ages
During the Middle Ages, blue was seen as a very insignificant color, especially in Europe. The wealthy and noble wore purple or red and it was only the poor who wore blue clothing, colored with low-quality dyes made from woad plants.
However, this changed later on between 1130 and 1140 when a French abbot rebuilt the St. Denis Basilica in Paris and had stained glass installed in the windows, colored cobalt. This gave the building a special look since the light shining through the red glass combined with the cobalt and filled the church with a heavenly bluish-violet light.
From then on, the color was known as ‘bleu de Saint-Dennis’ and blue stained glass was being installed in the windows of many other churches.
- Blue in Modern Times
Today, blue is the most popular color in the world, adored by many people, just like it was by the ancient Egyptians. It’s widely used in fashion and interior design and there are hundreds of different shades to choose from.
What Does the Color Blue Symbolize?

Blue, in its many shades, symbolizes a wide range of ideas. It often stands for tranquility, serenity, and calm, reminding us of the sky and sea. This brings feelings of peace and stability. In various cultures, people see blue as a symbol of trust, loyalty, wisdom, and confidence. You’ll find it in uniforms and symbols, where it promotes reflection and mental peace.
Blue also represents depth and infinity, like the endless sky or vast oceans. It’s linked to freedom, open spaces, and imagination, encouraging creative and broad thinking. However, blue can also express sadness or distance, as in the phrase “feeling blue.” Sometimes, it suggests conservatism and a reluctance to change.
In practical uses, blue is common in business for its professional and trustworthy vibe. In interior design, it’s popular for creating a calming and welcoming space. Blue is a flexible and important color in our world, representing everything from calmness and depth to wisdom and thoughtfulness.
Pros and Cons of the Color Blue

Blue, known for its depth and versatility, has both advantages and disadvantages. Positively, blue calms and soothes, making it great for creating peaceful spaces like bedrooms and hospitals. It’s ideal for relaxation. In business, blue often represents trust, reliability, and professionalism. Companies frequently use it in branding and uniforms to show dependability.
On the downside, blue can have negative effects. While it’s calming, it can also cause feelings of sadness, as the saying “feeling blue” suggests. This makes it less fitting for places needing energy and warmth.
Using dark blue too much can make spaces feel cold, unwelcoming, or too formal. Since blue is common in corporate environments, it can seem conventional or unoriginal, which might limit creativity in innovative settings.
In short, blue’s ability to calm and convey trust makes it a popular choice, but its association with sadness and its overuse in business can be drawbacks in some situations.
What Does the Color Blue Mean in Different Cultures?

In some culture the color blue has negative connotations whereas in others it’s quite the opposite. Here’s what this color means in different cultures worldwide.
1. Europe and North America
In Europe and North America, blue stands for trust, authority, and security. Businesses often use it in logos and uniforms to show professionalism and reliability. Blue’s calming nature makes it a favorite in healthcare and wellness areas.
It reminds people of the sky and water, creating a sense of openness and calm. However, blue also means sadness and isolation, as in “feeling blue” or “blue Monday.” This mix of meanings shows how deeply blue affects people in these regions.
2. Ukraine
In Ukraine, blue symbolizes good health and is a key part of the national flag, representing the sky and a sense of calm. It reflects the nation’s open skies and symbolizes freedom and hope.
Blue also connects to Ukraine’s agricultural heritage and natural resources, appearing in traditional clothing and art. It stands for health and tranquility, important considering Ukraine’s history and resilience.
3. Hinduism
In Hinduism, blue is deeply religious, especially linked to Lord Krishna. Krishna’s blue skin symbolizes his divine nature and the vastness of the sky and sea. In Hindu art and literature, blue shows Krishna’s divine presence and his role as a protector. It means spiritual joy, divine love, and eternal truth.
4. Greece
In Greece, blue represents the nation’s connection to the sea. The Greek flag’s blue and white symbolize the surrounding seas and waves. This color signifies freedom, exploration, and maritime history. It brings to mind Greek beaches, waves, and clear skies, showing national pride and Greece’s natural beauty and heritage.
5. African Cultures
In African cultures, blue symbolizes unity, love, peace, and harmony. It represents the sky and water, vital for life and community. Blue is common in traditional clothing and art, emphasizing community and togetherness.
Many African societies link blue to healing, wisdom, and spirituality. Its calming nature unites people during celebrations and reflection, showing the value of community and interconnected life in African cultures.
Personality Color Blue – What It Means

People who like the color blue often show calmness, stability, and depth in their personality. They are usually seen as trustworthy, reliable, and responsible. They look for peace and harmony in their surroundings and relationships. Blue personalities think deeply and like to have order and direction in their lives. They are loyal and sincere, making strong and meaningful connections with others.
Blue personalities stand out for their great communication skills. They listen well and give thoughtful advice. They handle situations calmly and logically, avoiding rash decisions. This trait makes them good at solving problems and reliable in both personal and work relationships.
However, their love for stability and order can make them resist change. They may find it hard to adapt to chaotic or unpredictable situations. Sometimes, their careful nature might come off as distant or unemotional.
People who favor blue value depth, sincerity, and calmness. They act as stable figures in their communities, providing a rational outlook. They’re quietly persistent and focus on building lasting relationships and stable structures.
Blue in Fashion and Jewelry

In fashion and jewelry, blue stands out for its unique and flexible charm. In clothing, blue ranges from classic navy, essential in both professional and casual outfits, to light pastels perfect for spring and summer.
This color brings a sense of reliability and elegance, appealing to both designers and shoppers. Blue can be eye-catching in bright shades or subtle and sophisticated in darker tones. Blue jeans, widely worn and loved, show how popular and adaptable blue is.
In jewelry, blue gems like sapphire, known for their deep and rich colors, are favorites for eye-catching pieces. They symbolize nobility and honesty. Lighter blue gems, such as aquamarine, create a feeling of calm and clarity, and are popular for their soothing effect. Turquoise and lapis lazuli add an exotic and vibrant touch, often seen in bohemian and unique designs.
Blue, linked with calmness, trust, and loyalty, is great for both everyday and special occasion wear. From a classic navy suit to a playful summer dress, or an impressive sapphire ring, blue keeps a timeless charm in fashion and jewelry, offering many ways to express style.
Wrapping Up
Cool and versatile, blue is an attractive color that looks great on most people. While the symbolism of the color can vary according to culture or religion, it remains a fashionable, soothing color that continues to be a favorite among many people.